6 Key Differences Between PVC Foam Board and Solid PVC Profiles
PVC materials are everywhere, but not all PVC products are the same. In extrusion manufacturing, PVC foam boards and solid PVC profiles are two very common product forms. They may share the same base material, yet their structure, performance, and applications can be very different.
If you’ve ever wondered why some PVC products feel lightweight while others feel extremely rigid, or why certain boards are better for furniture while others suit structural uses, this article will clear things up.
Let’s walk through the six key differences that really matter in daily use and production.
1. Internal Structure: Foamed vs Solid
The biggest difference starts on the inside.
-
PVC Foam Board:
Has a micro-cellular foamed structure inside. This creates tiny air pockets that reduce weight while maintaining shape. -
Solid PVC Profile:
Fully dense material with no internal voids, offering maximum strength and rigidity.
This internal structure affects almost everything else—from weight to strength to processing behavior.
2. Weight and Handling
Because of its foamed core:
-
PVC foam boards are significantly lighter
-
Easier to transport, cut, and install
-
More comfortable for manual handling
Solid PVC profiles, on the other hand, are heavier and more rigid. This extra weight is sometimes necessary, especially for load-bearing or structural applications.
For many users, lighter products simply make life easier, especially in furniture or decorative projects.
3. Strength and Load Performance
Here’s where the differences become very practical.
-
Solid PVC profiles offer higher mechanical strength
-
Better impact resistance and dimensional stability
-
Suitable for frames, supports, and structural components
PVC foam boards still have good rigidity, but they are not designed for heavy loads. They perform best when used as panels rather than structural elements.
So the question isn’t which one is stronger, but how much strength your application actually needs.
4. Surface Finish and Appearance
Both materials can achieve smooth surfaces through extrusion, but their final appearance can differ slightly.
-
PVC Foam Board:
-
Smooth, matte surface
-
Easy to laminate, print, or coat
-
Ideal for decorative finishes
-
-
Solid PVC Profiles:
-
More uniform density
-
Crisp edges and precise dimensions
-
Suitable for exposed functional components
-
This is why foam boards are commonly used in signage, cabinets, and interior panels, while solid profiles appear in doors, windows, and technical parts.
5. Machining and Fabrication
From a processing point of view:
-
PVC foam boards are easy to cut, drill, and screw
-
They behave more like wood-based panels
-
Solid PVC requires sharper tools and stricter control
Many fabricators prefer foam boards because they are more forgiving during secondary processing. Solid PVC profiles demand more precision, but the result is higher structural reliability.
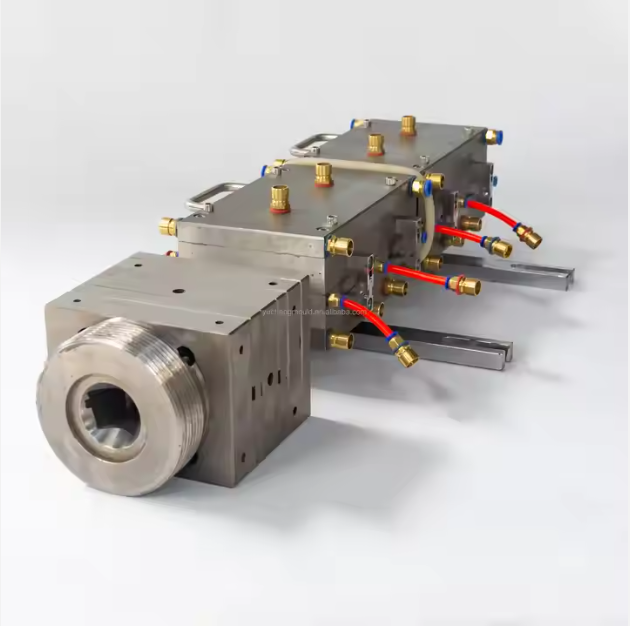
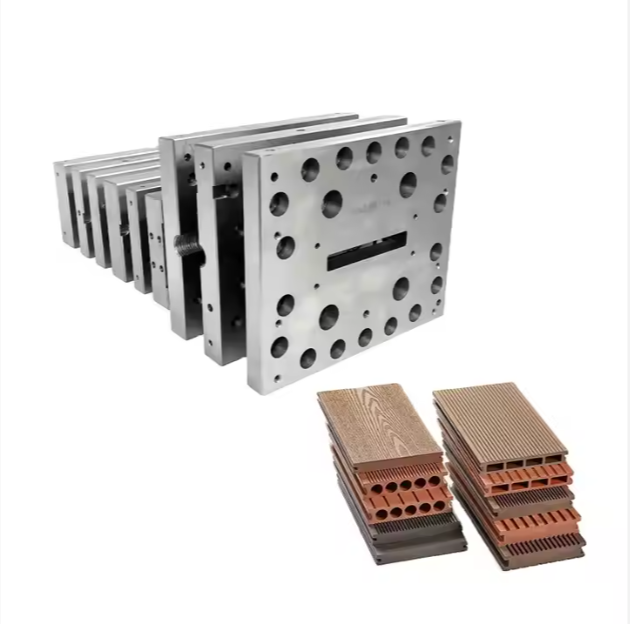
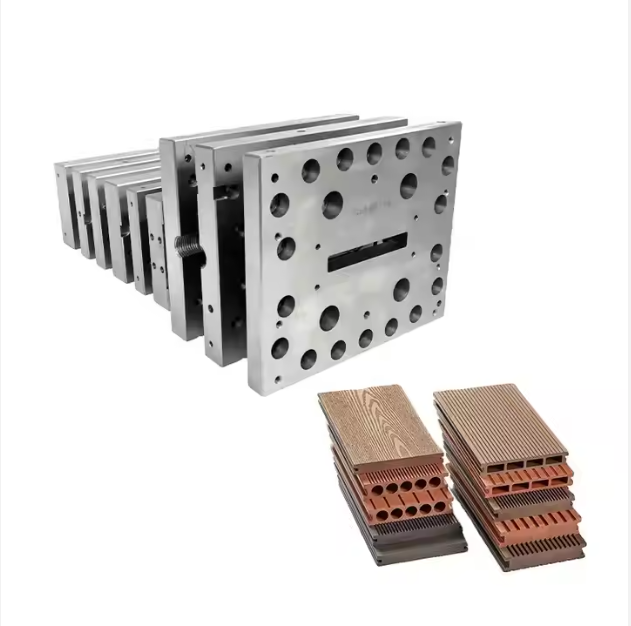
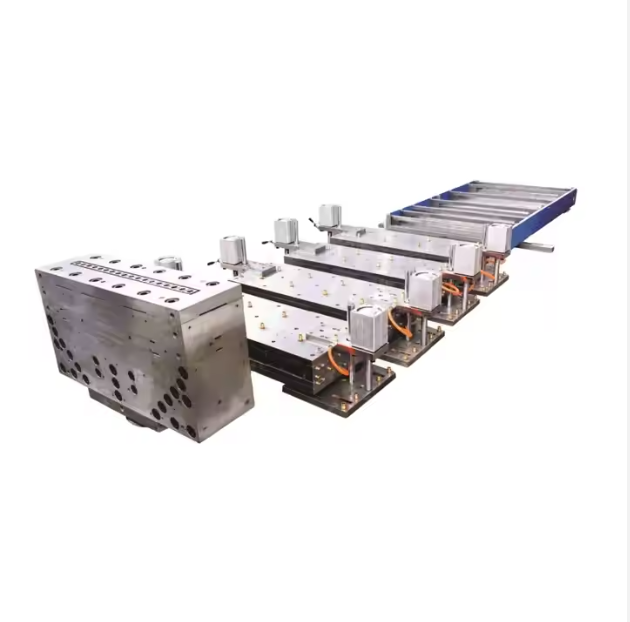
As discussed in earlier blogs, extrusion mould design plays a key role in achieving stable wall thickness and surface quality for both types.
6. Typical Applications in Daily Life
Let’s connect this to things people see every day.
PVC Foam Board is commonly used for:
-
Furniture panels and cabinets
-
Interior wall cladding
-
Advertising boards and displays
-
Decorative panels
Solid PVC Profiles are commonly used for:
-
Window and door frames
-
Electrical trunking
-
Technical industrial components
-
Structural decorative elements
You’ve probably interacted with both materials many times without realizing it. That’s how common they are.
How Extrusion Moulds Affect Both Products
Although the materials differ, both foam boards and solid profiles rely heavily on high-quality extrusion moulds. A well-designed mould ensures:
-
Stable material flow
-
Uniform thickness
-
Smooth surface finish
-
Reduced risk of defects
For PVC foam boards especially, mould design directly impacts foaming uniformity and final board density.
This ties back to our earlier discussions about material selection, extrusion stability, and mould precision.
Conclusion
PVC foam boards and solid PVC profiles are designed for different purposes, not to replace each other. Foam boards offer lightweight versatility and easy processing, while solid PVC profiles provide strength and durability where it matters most.
Understanding these differences helps manufacturers, designers, and end users choose the right solution—without overpaying or overengineering.
In extrusion, matching the material structure to the application is always the smartest approach.